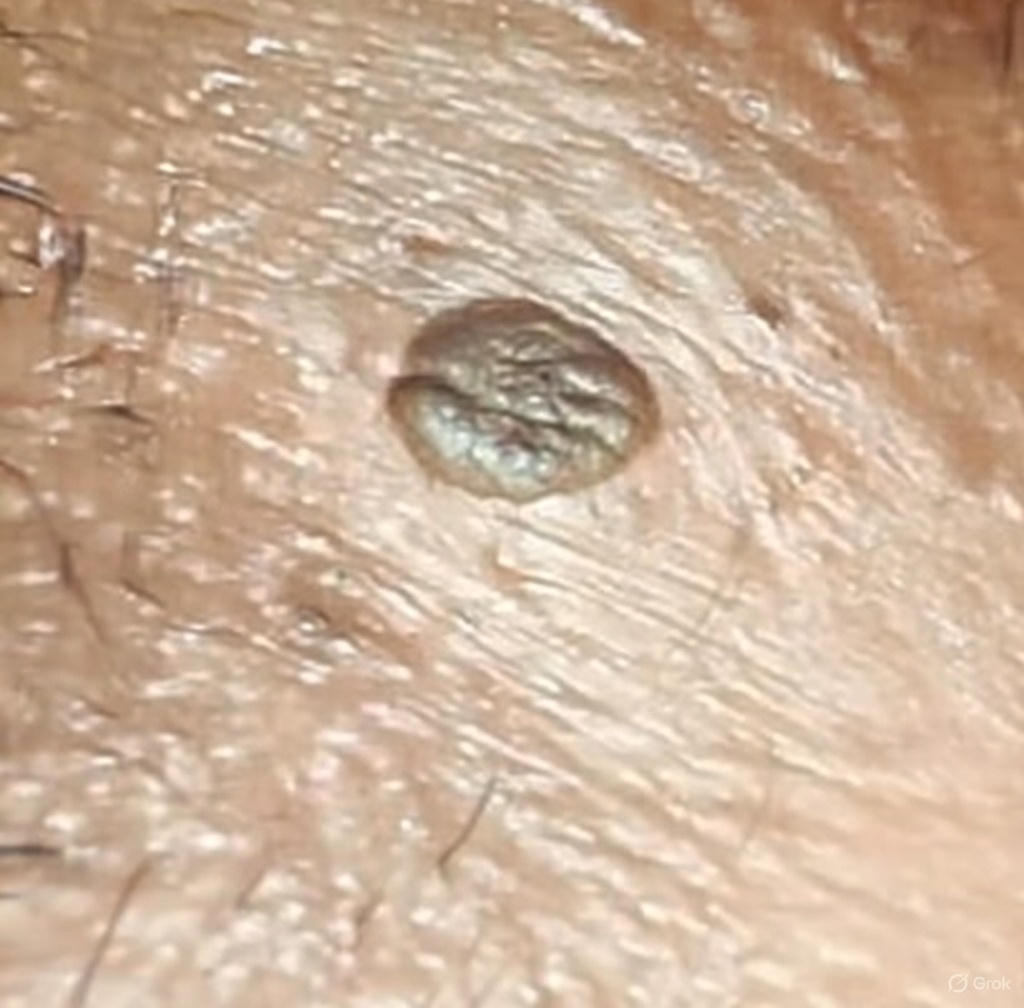
Genital Warts: Why They Come Back and What You Should Know
Genital warts are one of the most common sexually transmitted infections seen in clinics today. Many patients feel relieved when the warts disappear; only to feel frustrated or worried when they return.
If this has happened to you, you’re not alone.
Genital wart recurrence is common, and understanding why it happens can help reduce fear, stigma, and unnecessary anxiety.
What causes genital warts?
Genital warts are caused by the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), most commonly types 6 and 11. These are called low-risk HPV types because they cause warts but are not usually linked to cancer.
How common is recurrence?
Even after successful treatment:
- 30–60% of patients may notice warts returning within 3–6 months
- Recurrence is most common in the first year
- If no warts return after 12 months, the risk drops significantly
Importantly, recurrence does not mean treatment failed.
Why do genital warts come back?
1. Treatment removes the wart, not always the virus
Most treatments destroy visible warts, but HPV can remain hidden (latent) in nearby skin.
This means warts can reappear later, even without new sexual contact.
2. The immune system plays a big role
Your body’s immune system is what eventually controls and clears HPV. Factors that increase recurrence include:
- Stress
- Poor sleep
- Smoking and excessive alcohol
- Chronic illness
- HIV or other immune-suppressing conditions
3. Some treatments have higher recurrence rates
Different treatments work in different ways.
- Podophyllin paint – clears warts quickly but has higher recurrence
- Cryotherapy / TCA – moderate recurrence
- Topical cream – lower recurrence because it boosts immune response
- Surgical removal – lowest recurrence but more invasive
Treatments that stimulate the immune system reduce recurrence better.
4. Early sexual activity or untreated partners
- Sex before complete healing
- Inconsistent condom use
- Partners with untreated warts
All of these can increase the chance of recurrence.
How long does HPV stay in the body?
For most healthy adults:
- The immune system clears HPV naturally within 1–2 years
- During this time, warts may come and go
- Eventually, many people become wart-free permanently
How can recurrence be reduced?
Medical care
- Adequate initial treatment (not under-treating)
- Combining wart removal + immune-based therapy
- Proper follow-up appointments
Lifestyle and prevention
- Avoid sex until lesions fully heal
- Use condoms consistently
- Stop smoking
- Get enough sleep and manage stress
Does HPV vaccination help?
Yes.
Although the HPV vaccine does not treat existing warts, it:
- Reduces recurrence
- Prevents infection with new HPV types
- Is recommended even after wart treatment (age-appropriate patients)
When should recurrence be checked further?
You should return to the clinic if:
- Warts recur frequently
- They grow rapidly or become extensive
- They don’t respond to standard treatment
In some cases, doctors may recommend immune status testing, including HIV screening.
A message to patients
Genital wart recurrence:
- Is common
- Is not a sign of poor hygiene
- Is not proof of infidelity
- Does not mean you will have it forever
With proper care, follow-up, and time, most people eventually clear HPV completely.
How Mascot Healthcare can help
At Mascot Healthcare, we provide:
- Confidential genital wart evaluation and treatment
- Safe clinic-based procedures
- Home treatment guidance
- Recurrence prevention counseling
📍 Akoka, Yaba, Shomolu, Lagos
📞 Walk-in and appointment care available