Genital warts are one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs), yet many people don’t talk about them due to shame or misunderstanding. If you've heard about genital warts or think you might have them, here's what you really need to know.
What Are Genital Warts?
Genital warts are small growths or bumps that appear on or around the genitals, anus, or groin area. They are caused by certain types of the human papillomavirus (HPV)—specifically, low-risk strains like HPV types 6 and 11.
Where Can They Appear?
- On the vulva, vagina, or cervix (in women)
- On the penis or scrotum, (in men)
- Around the anus or in the rectum
- In some cases, even in the mouth or throat after oral sex
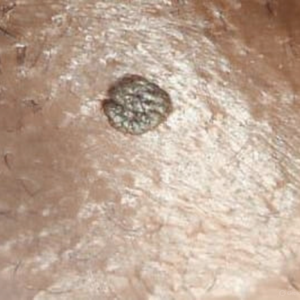
What Do They Look Like?
- Small, flesh-colored or gray growths
- Can be flat or raised, single or clustered (like cauliflower)
- Often painless, but may cause itching, discomfort, or bleeding during sex
Are Genital Warts Dangerous?
Most genital warts are not dangerous, and the HPV types that cause them do not lead to cancer. However:
- They can be embarrassing or emotionally stressful
- They may spread to sexual partners
- Other high-risk types of HPV (not the ones that cause warts) can lead to cervical or penile cancer—which is why regular screening is important
How Do You Get Genital Warts?
- Through vaginal, anal, or oral sex
- From skin-to-skin contact with an infected person
- Even if your partner has no visible warts, the virus can still be spread
It may take weeks or even months after exposure for warts to appear.
Treatment Options
There is no cure for the virus itself, but the warts can be treated or removed using:
- Topical creams
- Cryotherapy (freezing the warts off)
- Laser therapy or minor surgery for larger growths
Do NOT use over-the-counter wart removers meant for hands or feet—they can burn sensitive genital skin.
How to Prevent Genital Warts
- Use condoms during sex (though they don’t cover all skin areas)
- Get the HPV vaccine (e.g., Gardasil)—recommended for both males and females
- Avoid multiple sexual partners
- Regular STI screening and Pap smears (for women)
Final Thoughts
Genital warts are common, treatable, and not life-threatening; but they should not be ignored.
If you notice unusual bumps or growths in your private areas, early evaluation is important. At Mascot Healthcare Clinic in Lagos, we provide confidential assessment, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment in a safe, non-judgmental environment.
Take charge of your sexual health—click here to see a doctor or for genital wart treatment in lagos