Medical imaging has become an essential part of healthcare, helping doctors make accurate diagnoses and guide treatment. In Lagos, where access to diagnostic services is steadily improving, patients are often recommended to undergo scans such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans—but many are unsure of what these tests mean or how they differ.
Let us break down the key differences between ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans, their uses, and where you can access them in Lagos.
1. Ultrasound Scan (Sonography)
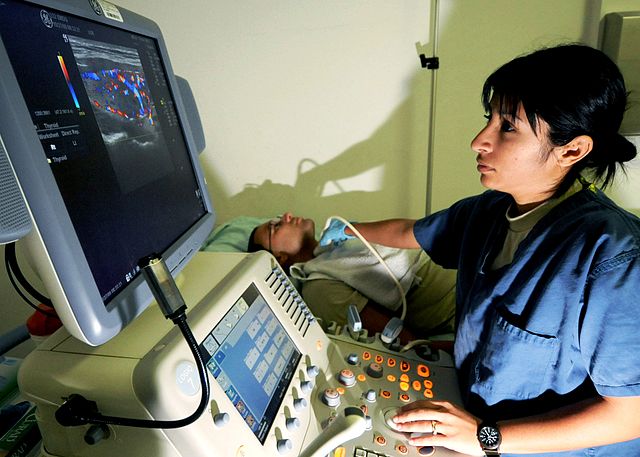
What it is:
An ultrasound scan uses high-frequency sound waves to produce live images of the inside of the body. It is non-invasive and does not use radiation.
Common Uses:
- Pregnancy checkups and monitoring fetal development
- Abdominal scans (liver, kidneys, bladder)
- Prostate, breast, and pelvic scans
- Soft tissue injuries and lumps
- Vascular scans (blood flow in veins and arteries)
Advantages:
- Safe for pregnant women and children
- Painless and quick
- Widely available and affordable in many clinics and diagnostic centres across Lagos
- Provides the most accurate diagnoses for many adult and children conditions.
Limitations:
- Cannot image bones or air-filled organs like the lungs
- Less detailed compared to MRI or CT for some medical conditions.
2. MRI Scan (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
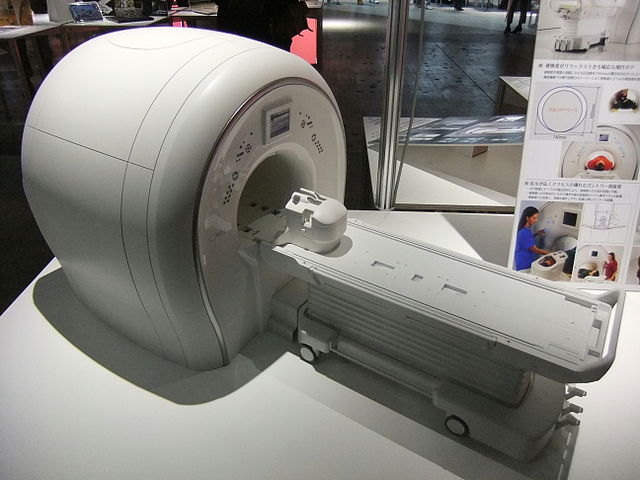

What it is:
MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate highly detailed images of organs and tissues. It does not use ionizing radiation.
Common Uses:
- Brain and spinal cord imaging
- Muscle and joint problems (e.g., imaging sports injuries)
- Tumor detection
- Soft tissue evaluation (e.g., ligaments, cartilage, nerves)
Advantages:
- Excellent for soft tissue contrast
- No radiation exposure
- Ideal for neurological, muscular, and joint imaging
Limitations:
- Very expensive and less available in public and private hospitals.
- Long scan times
- Cannot be used in patients with certain metal implants or pacemakers
3. CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
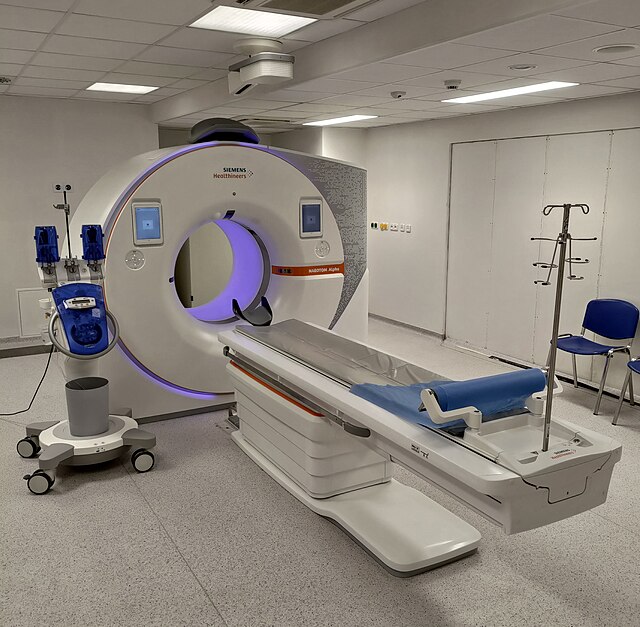
What it is:
CT scans use X-rays and computer technology to produce cross-sectional images (slices) of the body. It is more detailed than regular X-rays.
Common Uses:
- Head injuries and stroke assessment
- Chest and lung conditions
- Abdominal pain and trauma
- Bone fractures and tumors
- Cancer staging
Advantages:
- Fast and accurate
- Excellent for emergency cases
- Provides detailed images of bones, lungs, and blood vessels
Limitations:
- Exposure to radiation
- Much more expensive than ultrasound, but not as expensive as MRI
- Not suitable for routine use in pregnant women
Choosing the Right Scan
The right scan depends on your symptoms, doctor’s recommendation, and affordability:
- Ultrasounds are the most commonly used due to accessibility and cost.
- CT scans are ideal for emergency and trauma settings.
- MRI scans are preferred for neurological and soft tissue evaluations but are more costly.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the differences between these scans helps patients make informed decisions and reduce anxiety. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional to know which imaging test is right for you. Early diagnosis saves lives—don’t delay your scan if your doctor recommends one.