Missed Abortion: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
A missed abortion, also known as a missed miscarriage, occurs when a fetus stops developing but remains in the uterus without immediate signs of pregnancy loss. Unlike a typical miscarriage, there may be no noticeable symptoms such as bleeding or cramping, making it difficult to detect without medical evaluation.
Causes and Risk Factors
Missed abortion often results from genetic abnormalities that prevent proper fetal development. Other factors include hormonal imbalances, maternal infections, underlying health conditions like diabetes, and lifestyle factors such as smoking or excessive alcohol use.
Symptoms
Most women do not experience obvious signs, but some may notice:
- A sudden loss of pregnancy symptoms (e.g., nausea, breast tenderness)
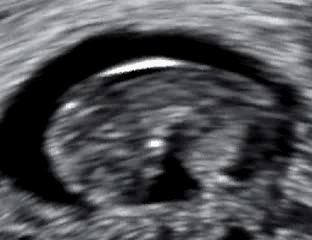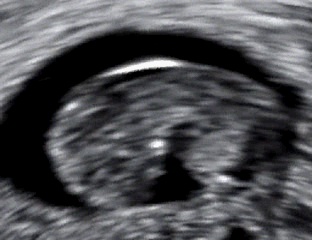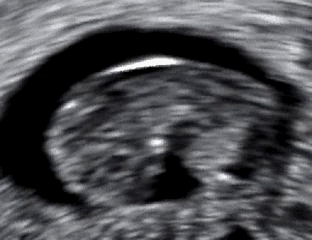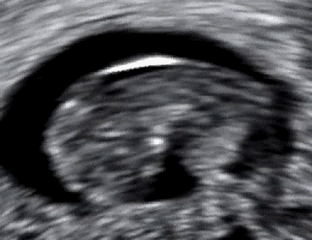
- No fetal heartbeat detected on ultrasound
- A uterus that does not grow as expected
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosis is typically confirmed through ultrasound, showing no fetal heartbeat or halted growth. Management options include:
- Expectant Management – Allowing the body to expel the pregnancy naturally
- Medication – Inducing uterine contractions to pass the pregnancy
- Surgical – Removing the tissue from the womb via a minor procedure
Emotional and Physical Recovery
A missed abortion can be emotionally distressing. Counseling, support groups, and medical follow-up are essential for both physical and mental well-being.
If you suspect a missed abortion, consult a healthcare provider promptly for appropriate care and support.