Adenomyosis, a common gynecological disorder characterized by the abnormal presence of endometrial tissue within the myometrium, poses diagnostic challenges due to overlapping symptoms with other uterine conditions. While magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is traditionally considered the gold standard for adenomyosis diagnosis, recent studies have focused on transvaginal and pelvic ultrasound as a cost-effective and accessible alternative. This article provides a comprehensive review of sonographic features associated with adenomyosis, shedding light on their diagnostic significance and potential clinical implications.
Bulky Uterus:
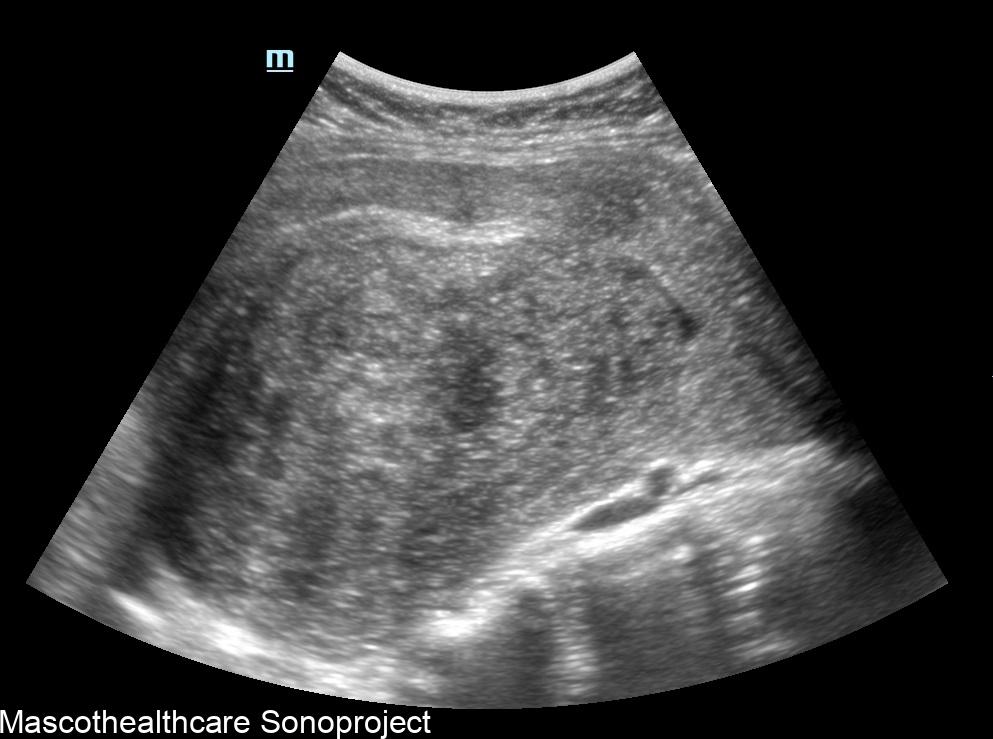
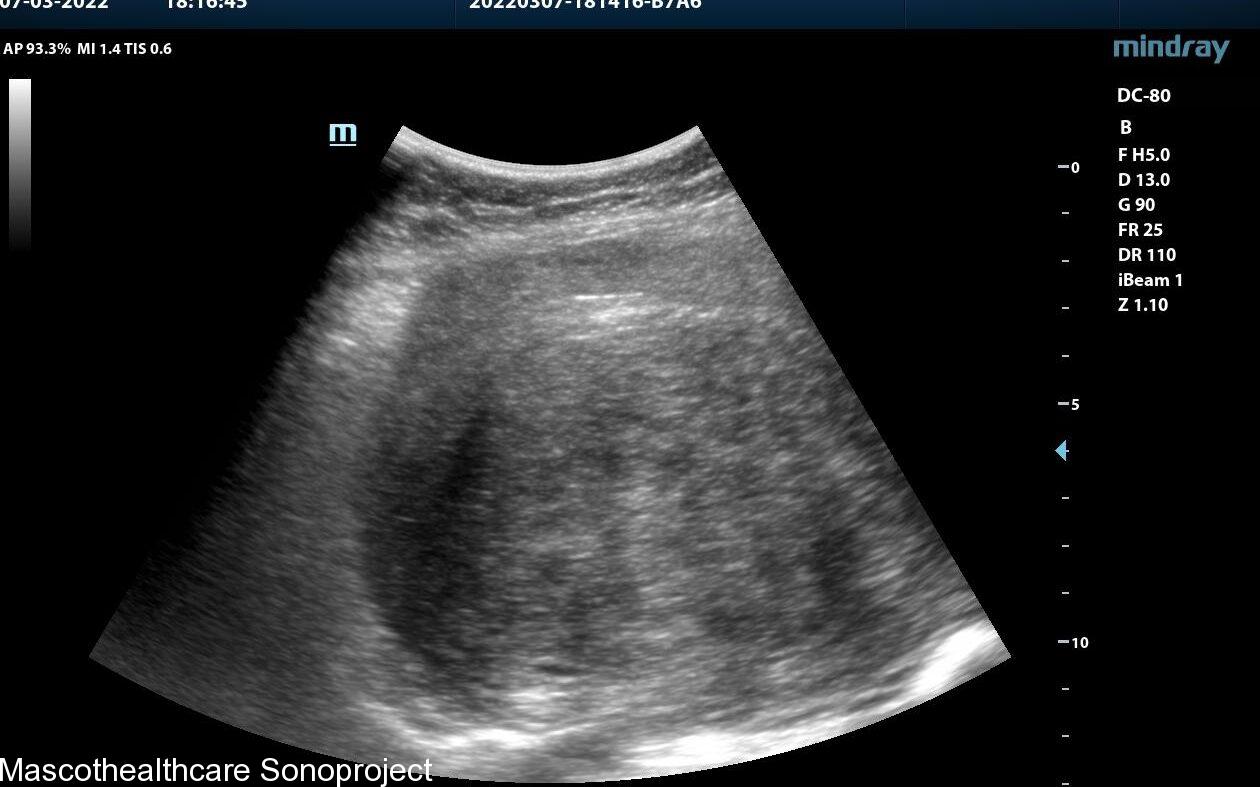
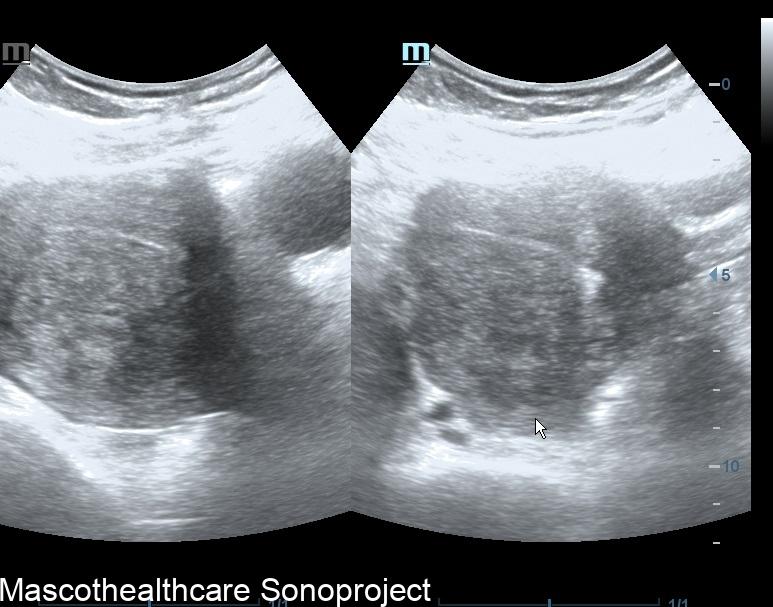
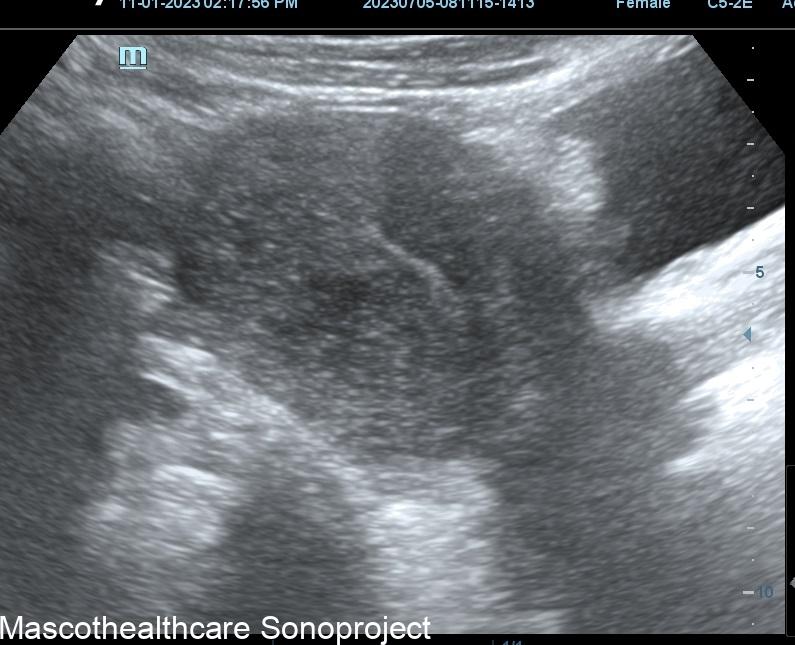
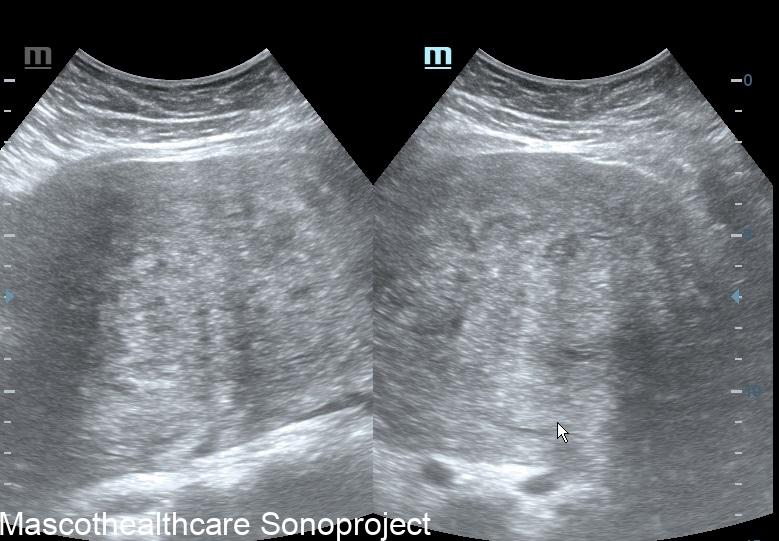
One of the primary sonographic features associated with adenomyosis is a "bulky uterus." This is usually a diffuse or posterior wall thickness usually devoid of definite uterine mass.
Heterogeneous Myometrium:
The presence of a "heterogeneous myometrium" is another key sonographic feature linked to adenomyosis. Transvaginal ultrasound allows for the visualization of irregularities in the myometrial texture, reflecting the infiltration of endometrial tissue. This feature, when assessed independently, has demonstrated a mean sensitivity and specificity both surpassing 50%, making it a valuable indicator for clinicians.
Myometrial Cysts:
The formation of myometrial cysts, visualized through ultrasound, has been recognized as a sonographic feature indicative of adenomyosis. These cystic structures within the myometrium contribute to the heterogeneous appearance detected during imaging. Although the specificity of myometrial cysts may vary, their inclusion in a comprehensive assessment of sonographic features strengthens the diagnostic process.
Endometrial–Myometrial Interface Ill-Definition:
A crucial sonographic feature in adenomyosis diagnosis is the "ill-definition of the endometrial–myometrial interface." This refers to a lack of clear demarcation between the endometrial and myometrial layers, often observed during ultrasound examinations. The reviewed study identified this feature as a significant contributor to diagnostic accuracy, especially when combined with other indicators.
Echogenic Linear Striations:
Echogenic linear striations, visualized through ultrasound imaging, have been associated with adenomyosis. These linear patterns form the typical venetian blind shadowing pattern.
Uterine myoma may also coexist with adenomyosis but a commonly observed feature is a bulky uterus with a size that cannot be explained by the relatively smaller myoma.

Informative article