Who Should Take the HPV Vaccine?
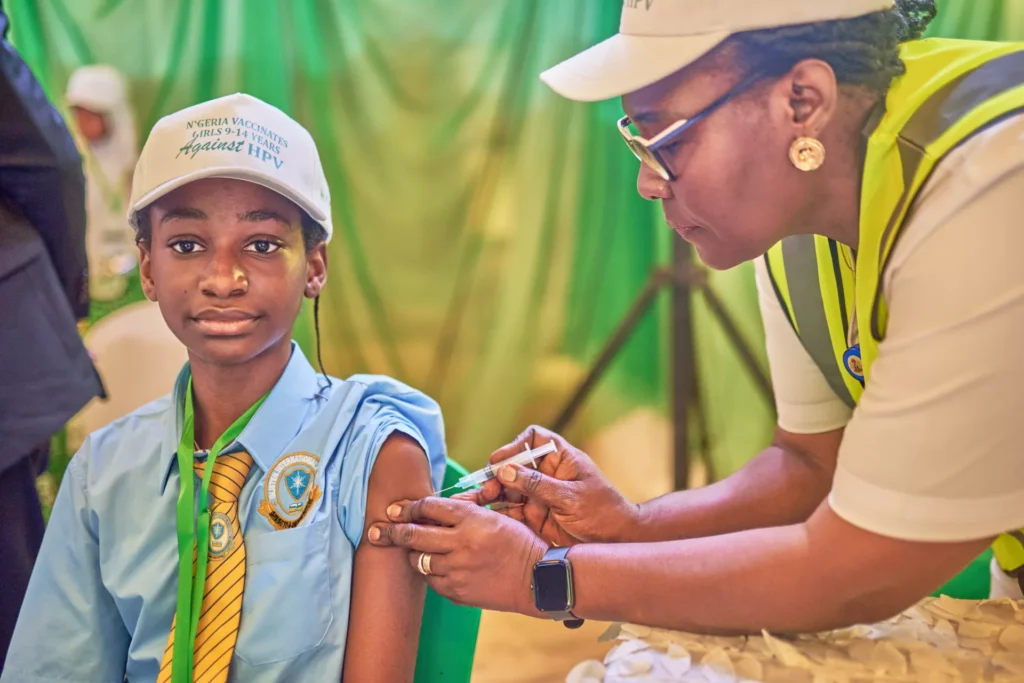
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common virus that can lead to several types of cancers, including cervical, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers. The HPV vaccine is a crucial tool in preventing these infections and their complications. But who should get the HPV vaccine, and when?
1. Preteens and Adolescents The ideal age for receiving the HPV vaccine is between 9 and 14 years. It is recommended that both boys and girls get vaccinated before they become sexually active. The immune response is stronger when the vaccine is administered at a younger age, providing better protection against HPV-related conditions.
2. Teenagers and Young Adults (15-26 years) If not vaccinated earlier, teenagers and young adults can still benefit from the vaccine. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends catch-up vaccination for individuals up to age 26 who did not receive the vaccine when younger.
3. Adults (27-45 years) While the vaccine is FDA-approved for adults up to 45 years old, it is typically recommended for those at continued risk of HPV exposure who were not adequately vaccinated earlier. Consultation with a healthcare provider can help determine if vaccination is appropriate in this age range.
4. Individuals with Weakened Immune Systems People with weakened immune systems, including those living with HIV, should consider getting vaccinated, as they may be more susceptible to persistent HPV infections and related complications.
5. Men and Women Both males and females can benefit from the HPV vaccine. Vaccinating males helps prevent the spread of the virus and reduces the risk of HPV-related cancers and genital warts in men.
Who Should Not Take the HPV Vaccine?
- Individuals who have had a severe allergic reaction to a previous dose or any component of the vaccine.
- Pregnant individuals are generally advised to delay vaccination until after delivery.
Conclusion The HPV vaccine is a safe and effective way to protect against HPV-related cancers and infections. Early vaccination offers the best protection, but it can still be beneficial for those up to age 45 in certain circumstances. Speak with your healthcare provider to determine the best vaccination plan for you or your family.